THE SKIN
ANATOMY
The skin is composed of a number of layers. The outermost layer is called the epidermis – the cells at the bottom of the epidermis move upwards, die during the movement and create a layer of dead cells that are called the stratum corneum. This is the coating that we feel when we touch our skin. The corneum flakes off all the time and is replaced by new cells, and is used as a protective layer. Under the epidermis lies the dermis – this layer contains many fibers of an elastic material and of the protein collagen. The changes in these materials occur during aging of the skin and as a result, wrinkles and folds are created. The dermis contains blood vessels that feed the skin, sweat glands that give off sweat, sebaceous glands that give off fatty matter that covers the skin, hair follicles and sensitive receptors of the various senses. Under the dermis is found the hypodermis, which is the body’s fatty layer.
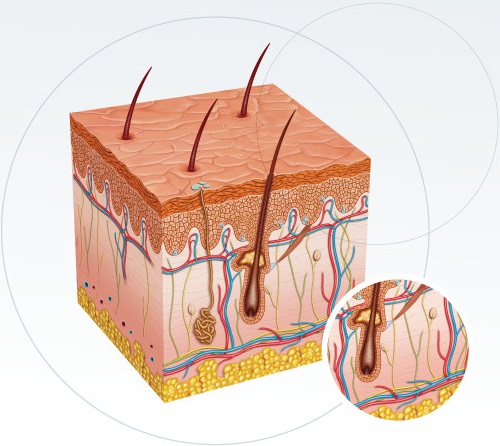
Blood Vessels
numerous blood vessels make up the arteries underneath the sub-dermal layer, and they make up the plexus cutaneous, located between the dermis and the hypodermis. The blood vessels have a twisted path and branch out at the bottom of the papillary layer.
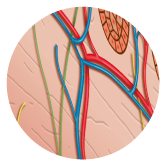
epidermis
outer layer without blood vessels, made up of five different layers of cells that are meant especially for protection, stability and sealing. The most extreme layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum, is removed in a continuous, natural process of peeling, the cells first make their way from the deep layers of the skin. (The process of cornification takes 30 days).
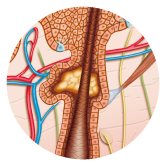
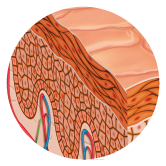
sebum
Glades Sebaceous opens into the follicles of Hair follicles. The sebum is made up of a mixture of fats, cells and free acids, soothes the skin and hair and protects them from dehydration.
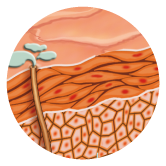
dermis
This layer is rich in blood vessels and nerves, and is divided into two: The Papillare Stratum is connected to the epidermis by the connective tissues or papillae and is full of capillaries that feed the epidermis. The connective tissue contains fibrocytes that are filled with elastic collagen fibers. The intercellular space is filled with a gel-like substance, where blood cells and tissue can move. The Reticulare Stratum contains strong interwoven collagen fibers, and between them nets of elastic fibers – this structure gives the skin its elasticity. The skin’s fold lines are created in places where the skin is the least elastic.
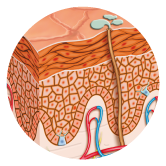
collagen
the production of the fibers starts in fibroblasts. The fibroblasts release a spiral made of amino acids into the cell, which first turns into very thin fibers of insoluble collagen and at the end they join into collagen fibers.
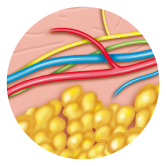
hypodermis
the deepest layer of the skin, enclosed by the connective strands of the muscles or bones. In this sub-cutaneous tissue, one can find fat with insulating, storage and shaping properties.
